Styrene Monomer
Chemical Formula:C8H8 CAS Registry Number : 100-42-5
Styrene monomer, under ambient conditions is a colourless clear liquid with a distinctive sweetish aromatic odour. It is miscible with most organic solvents in any ratio and is a good solvent for synthetic rubber, polystyrene and other high molecular weight polymers. From the environmental impact point of view, it is only slightly soluble in water (approx. 300 ppm at ambient conditions) and consequently the acute hazard of spilled styrene will be very limited for most aquatic species. However styrene may cause tainting (unpleasant taste) in food from aquatic organisms exposed to low environmental concentrations. According to the Standard European Behaviour Classification (Bonn Agreement) styrene is classified as a “floater evaporator”.
Productions
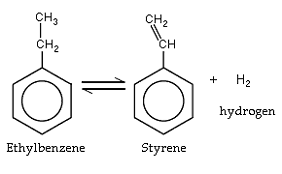
The conventional method for producing styrene involves two steps: the alkylation of benzene with ethylene to produce ethyl benzene followed by dehydrogenation of the ethyl benzene to produce styrene. Over the almost fifty years of practicing the conventional two step process refinements have constantly been made to improve conversion and selectivity to ethyl benzene and finally to styrene along with design changes to conserve and utilize the energy in particular from the exothermic alkylation step. The traditional aluminum chloride catalyst used in this alkylation is slowly being replaced by zeolite catalyst technology. Currently the predominant route for the commercial production of styrene is by dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene in the presence of steam over a catalyst (iron oxide) in either fixed bed adiabatic or tubular isothermal reactors. Another route involves co-production of styrene and propylene oxide via hydroperoxidation of ethyl benzene. Limited scale extraction from steam cracker pyrolysis gasoline is also practised.
PDF VERSION