  |
 |
Description
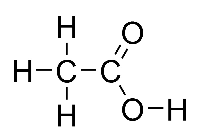
Acetic acid, CH3COOH, also known as ethanoic acid, is an organic acid, which gives vinegar its sour taste and pungent smell. It is a weak acid, in that it is only a partially dissociated acid in an aqueous solution. Pure, water-free acetic acid (glacial acetic acid) is a colourless liquid that absorbs water from the environment (hygroscopy), and freezes at 16.5 °C (62 °F) to a colourless crystalline solid. The pure acid, and concentrated solutions, are dangerously corrosive. |
|
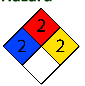
Hazards
NFPA 704 EU Classification |
Applications Acetic acid is a chemical reagent for the production of chemical compounds. The largest single use of acetic acid is in the production of vinyl acetate monomer, closely followed by acetic anhydride and ester production. The volume of acetic acid used in vinegar is comparatively small. |
|
|
Risk Phrases: R10, R35
Safety Phrases: (S1/2), S23, S26, S45
|
In the form of vinegar, acetic acid solutions (typically 4% to 18% acetic acid, with the percentage usually calculated by mass) are used directly as a condiment, and also in the pickling of vegetables and other foodstuffs. Table vinegar tends to be more diluted (4% to 8% acetic acid), while commercial food pickling generally employs more concentrated solutions. The amount of acetic acid used as vinegar on a worldwide scale is not large, but historically this is by far the oldest and most well-known application. Tapatío hot sauce is an example of a product that combines acetic acid and water to create vinegar in the production of the food product. |