Plypropylene Glycol
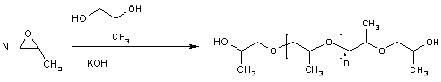
Chemical Formula : H[OCH(CH3)CH2]nOH CAS Registry Number 25322-99-4
| Polypropylene glycol or polypropylene oxide is the polymer of propylene glycol. Chemically it is a polyether. The term polypropylene glycol or PPG is reserved for low to medium range molar mass polymer when the nature of the end-group, which is usually a hydroxyl group, still matters. The term "oxide" is used for high molar mass polymer when end-groups no longer affect polymer properties. In 2003, 60% of the annual production of propylene oxide of 6.6×106 tonnes was converted into the polymer. |
 |
Property PPG has many properties in common with polyethylene glycol. The polymer is a liquid at room temperature. Solubility in water decreases rapidly with increasing molar mass. Secondary hydroxyl groups in PPG are less reactive than primary hydroxyl groups in polyethylene glycol. |
|
Polymerization Polypropylene glycol is produced by anionic ring-opening polymerization of propylene oxide. The initiator is an alcohol and the catalyst a base, usually potassium hydroxide. When the initiator is ethylene glycol or water the polymer is linear. With a multifunctional initiator like glycerine, pentaerythritol or sorbitol the polymer branches out. |
Uses PPG is used in many formulations for polyurethanes. It is used as a rheology modifier.PPG is also employed as a tuning reference in mass spectrometry.PPO is used to sterilize or pasteurize nutmeats, notably almonds. |
|
|
Conventional polymerization of propylene oxide results in an atactic polymer. The isotactic polymer can be produced from optically active propylene oxide, but at a high cost. A salen cobalt catalyst has recently been reported to provide isotactic polymerization of the racemic propylene oxide. |