ETHYL ACETATE (C4H8O2)
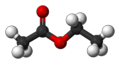
Chemical Structure
|
|
DESCRIPTION :
|
|
| Hazards | |||

NFPA 704
|
EU Classification
|
Productions: Ethyl acetate is synthesized industrially mainly via the classic Fischer esterification reaction of ethanol and acetic acid. This mixture converts to the ester in about 65% yield at room temperature:CH3CH2OH + CH3COOH ⇌ CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2OThe reaction can be accelerated by acid catalysis and the equilibrium can be shifted to the right by removal of water. It is also prepared industrially using the Tishchenko reaction, by combining two equivalents of acetaldehyde in the presence of an alkoxide catalyst:2 CH3CHO → CH3COOCH2CH3 |
|
|
Uses Ethyl acetate is primarily used as a solvent and diluent, being favored because of its low cost, low toxicity, and agreeable odor. For example, it is commonly used to clean circuit boards and in some nail varnish removers (acetone and acetonitrile are also used). Coffee beans and tea leaves are decaffeinated with this solvent. It is also used in paints as an activator or hardener.Ethyl acetate is present in confectionery, perfumes, and fruits. In perfumes, it evaporates quickly, leaving but the scent of the perfume on the skin. |
|||